WATCH – MORE SUNSCREEN PLEASE! –
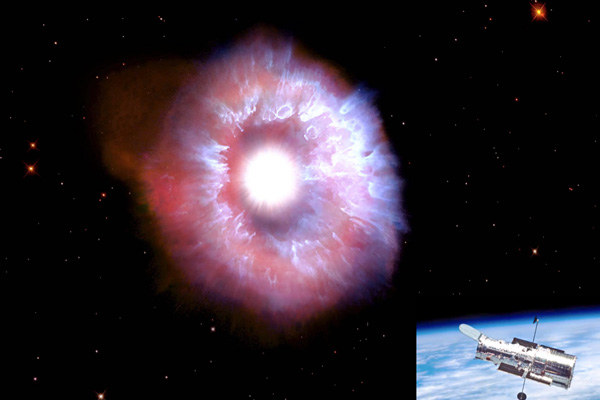
April 23, 2021 – The expanding shell of gas and dust that surrounds the star is about five light-years wide, which equals the distance from here to the nearest star beyond the Sun, Proxima Centauri.
The huge structure was created from one or more giant eruptions about 10,000 years ago. The star’s outer layers were blown into space—like a boiling teapot popping off its lid. The expelled material amounts to roughly 10 times our Sun’s mass. These outbursts are the typical life of a rare breed of star called a luminous blue variable, a brief convulsive phase in the short life of an ultra-bright, glamorous star that lives fast and dies young. These stars are among the most massive and brightest stars known. They live for only a few million years, compared to the roughly 10-billion-year lifetime of our Sun. AG Carinae is a few million years old and resides 20,000 light-years away inside our Milky Way galaxy.
Luminous blue variables exhibit a dual personality: They appear to spend years in quiescent bliss and then they erupt in a petulant outburst. These behemoths are stars in the extreme, far different from normal stars like our Sun. In fact, AG Carinae is estimated to be up to 70 times more massive than our Sun and shines with the blinding brilliance of 1 million suns.
“I like studying these kinds of stars because I am fascinated by their instability. They are doing something weird,” said Kerstin Weis, a luminous blue variable expert at Ruhr University in Bochum, Germany.